Strong supplier market in East Asia
With Corona impacting in China and rests of the world, our Shanghai team has conducted the market research of automotive industry in East Asia:
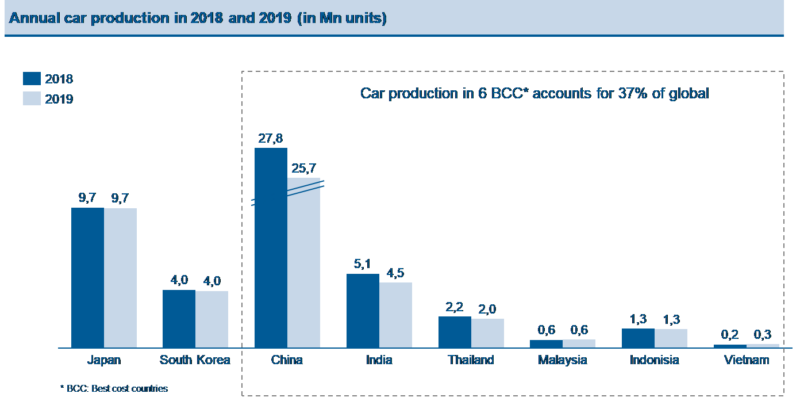
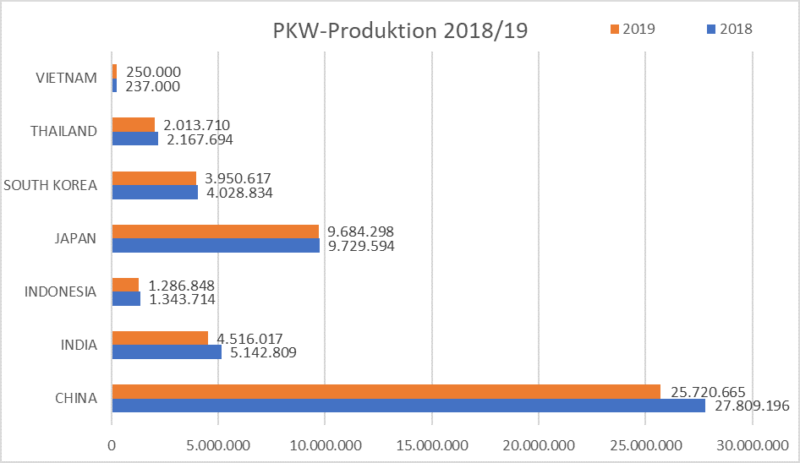
In 2019, led by China, Japan, India, and Korea, Asia remains the largest hub for automotive manufacturing with 48 million units produced, which accounted for more than half of the world.
(Source: Organisation Internationale des Constructeurs d’Automobiles – OICA)
This not only reflects the great market demand in Asia, but also maturity in the local supply chain. The manufacturing and assembly capabilities in Asia are not only securing local market, but also contribute to the global export.
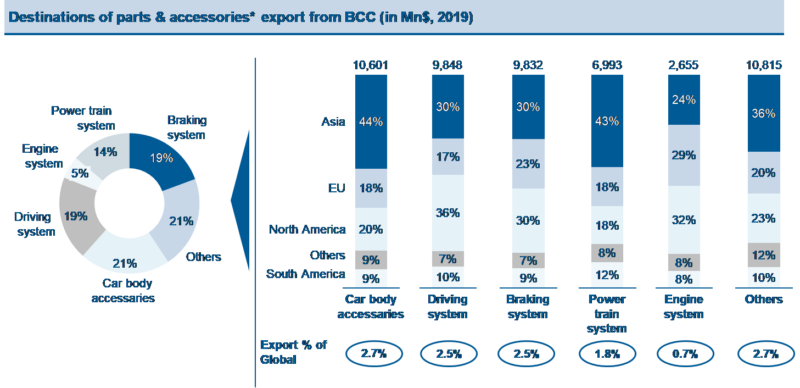
If looking at parts and accessories, export from Asia contributed 29% to global, among which China, India and other 4 BCCs (Best Cost Countries) accounted for 13%. Further looking at the BCCs, Car body accessories, Driving system, Braking system, Powertrain system and the Engine system are the top 5 exporting categories by value. While Driving system, Braking system and Engine systems are with the highest export value to Europe and North America. Parts in such categories are well worthy sourcing from Asia.
(Source: Germany Trade and Invest – GTAI)
Eyes on future, countries are pushing for different strategies in Automotive. This will change the existing division of labor in the automotive industry in Asia. The INVERTO team in Shanghai is keeping a close eye on developments, with a particular focus on the supplier market.
Strategic Goals in Automotive Production
- China: Forcing ambitious environmental standards both for production and for the cars themselves
- Japan: Rewards companies that relocate their production back to the domestic market or to the ASEAN region with tax breaks.
- South Korea: Promotes alternative drive systems – both electric and hydrogen – and autonomous driving.
(Source: Organisation Internationale des Constructeurs d’Automobiles – OICA)
India, Thailand, Indonesia and Vietnam have been successful in developing their automotive industries in recent years. While the focus for all four countries is on production for the Asia-Pacific region, they all also supply a share of their automotive products to Europe. Relations could become even closer in the future.
India
Almost every third small car worldwide is produced on the subcontinent. The large, globally active supplier companies are correspondingly well represented in India. Overall, the automotive industry contributes around 7% to the gross domestic product. The industry has expanded strongly in recent years: in 2018, 36% more cars were produced than five years previously.
The shift away from the internal combustion engine is a challenge for the Indian automotive sector. In order to get a grip on increasing air pollution, the state is promoting electromobility, but so far with little success. There are also plans to enter battery production. Through the government’s Automobile Mission Plan 2016 – 2026, it is envisaged making India one of the top three automobile manufacturing centers.
Thailand
With around two million vehicles, Thailand is the largest car producer among the ten ASEAN countries. The country wants to develop into a research and development center for the automotive industry, but is still quite a long way from achieving this goal. Although numerous international manufacturers and suppliers are represented in Thailand, so far they have mainly assembled kits that are imported. Production is not only for the country itself, but also for export to other Asian countries and Australia.
The government is strongly promoting electromobility, but the interest of the local population is currently still limited due to a lack of charging infrastructure. However, since companies see export opportunities, both manufacturers and suppliers are investing in e-mobility. In addition, a battery center is being built, in which the German TÜV is also participating. The center will research battery and storage technology under tropical conditions.
Indonesia
The Indonesian automotive industry is dominated by Japanese manufacturers and suppliers who assemble locally or have commissioned local companies to assemble kits. The entire automotive sector is predominantly located in West Java.
The government promotes economical small cars and electric cars. The background to this is that gasoline and diesel must be imported, while electricity can be produced cheaply with domestic coal and, moreover, nickel is mined in Sulawesi. So far, however, no company has been convinced to invest in battery production in this remote region.
Vietnam
Vietnam currently still plays a minor role in the automotive industry. So far, mainly finished parts are imported and assembled on site. The government wants to change this and is strongly encouraging manufacturers and suppliers – this applies to cars with conventional engines as well as to e-mobility. Since 2018 there is also a local car manufacturer: Vinfast currently produces vehicles with combustion engines, but an electric car is under development.
Development could receive a boost from the Corona pandemic. In the wake of the crisis, Japanese manufacturers are restructuring their supply chains – according to a survey by the Japanese Automobile Association, a good 40% of those surveyed now want to invest in Vietnam.
Our experts will be glad to address any inquiries you might have.
Get in touch with our experts now:
[contact-form-7 id=”2901″ title=”Kontaktformular EN”]